The domain name market has evolved from subjective, human valuations of domain names into a sophisticated data-driven industry where artificial intelligence plays an increasingly critical role.
At the core of AI-driven domain appraisals lies the power of machine learning and predictive analytics: these technologies empower AI to process vast datasets, recognize patterns, and forecast future trends with precision.
In this article we explore how AI is revolutionizing domain valuation, how it benefits domain resellers, as well as the challenges involved and the roadmap that makes artificial intelligence a useful component for modern appraisal.
Evolution of domain valuation methods
Domain valuation has historically relied on heuristic approaches and expert judgment, making the process inherently subjective and variable. Before AI integration, domain appraisers assessed factors such as length, keyword relevance, and potential traffic manually, resulting in inconsistent valuations across the industry
The transition to algorithmic valuation began with basic statistical models but has since evolved into sophisticated AI systems capable of processing millions of data points to identify complex patterns and relationships that human experts might miss.
Following up, let’s deep dive into the foundational technologies making modern domain valuation possible.
AI Technologies driving modern domain valuation
Beyond its capacity to handle vast datasets, AI stands out in domain valuation by leveraging advanced techniques that decipher complex variables and their interconnections.
Among the technologies and techniques involved in the process we see critical components of AI systems, like Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing.
Machine Learning (ML)
At the core of AI-powered domain valuation are machine learning algorithms designed to analyze historical sales data and identify patterns that correlate with domain values.
These systems process thousands or even millions of past domain transactions to recognize the factors that consistently influence domain prices.
With machine learning and predictive analytics, AI-driven domain valuation transforms the process by analyzing vast datasets, identifying hidden patterns, and forecasting potential market trends. AI evaluates multiple dynamic variables (like search volume, backlink quality, social signals, and comparative domain sales) to deliver more accurate and real-time insights.
MLs also impact keyword research systems and keyword-based valuation: they are the foundation for analytical SEO tools, which serve to identify and predict the performance of query searches, useful in organic growth strategies for domains.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Domain names fundamentally represent linguistic constructs, making natural language processing a critical technology in their evaluation.
Modern AI appraisal systems leverage NLP to analyze semantic meaning, brandability, and memorability of domain names, factors that significantly impact their market value
Recurrent neural network (RNN)
RNNs are artificial neural networks designed to process sequential data, such as text, speech, and time series.
Because of this, they excel at analyzing domain names as structured sequences of characters or tokens. Their ability to retain contextual memory allows them to:
- Capture linguistic dependencies
- Model temporal trends in historical sales data to predict future valuations
- Handle variable-length domain names by processing inputs step-by-step
In this breakdown, let’s observe how RNNs can solve common challenges related to domain valuation:
| Challenge | RNN-Driven Solution |
| Ambiguous tokenization | Web-crawled training data resolves splits using website content |
| Market volatility | Continuous retraining on fresh sales data adapts to trends |
| Multi-source pricing | Context-aware modeling separates domain value from marketplace biases |
From intuition-based to data-driven decisions
Data-driven dynamics in appraisal and valuation systems begin with the localization, recognition and categorization of information.
This is the phase where data ingestion and preprocessing happen.
Thus, before any analysis can occur, AI valuation systems must ingest and normalize diverse data sources.
This raw data undergoes preprocessing to standardize formats, remove outliers, and extract relevant features for the AI to analyze: the quality of this preprocessing significantly impacts the final valuation accuracy.
In this way, AI systems can tokenize domains and convert them into a vector form, which encapsulates their linguistic and market attributes. Thus, tokens can be words, subwords, or characters.
Algorithms rationale
Modern domain valuation systems typically employ ensemble approaches that combine multiple algorithmic techniques:
- Supervised learning models trained on historical sales data to predict valuations based on identified patterns.
- Deep learning neural networks that process domain names as sequences, identifying complex linguistic patterns that correlate with value.
- Comparative market analysis algorithms that identify similar previously sold domains to establish value ranges.
- Predictive modeling to forecast domain value trends based on market movements and emerging patterns.
With this, an AI-based appraisal process breaks down into several factors that affect the estimated value of domains.
Appraisal engineering and determining factors
AI domain valuation systems analyze numerous factors to determine a domain’s worth. These typically include:
- Domain length and composition: shorter domains generally command higher values, with premium status typically assigned to dictionary words and brandable terms.
- Keyword relevance and search volume: domains with content containing well-researched keywords hold greater potential value, which AI systems assess by analyzing search engine data and keyword competition metrics.This rationale doesn’t only rely on the search volume, but also on a variety of other factors, including the organic “difficulty” for a query to rank on search engines for a certain geographical market.
- Domain extension: the type of TLD significantly impacts value, with AI systems learning the relative importance of extensions like .com versus newer options like .AI.
As explored in this article, .AI domains are gaining significant traction and represent a valuable opportunity for domain investors.
- Traffic and SEO metrics: historical traffic data, including search engine rankings, backlink profiles, domain authority, spam score, and user engagement metrics provide signals about a domain’s established audience, impacting its final value.
- Market trends and sector analysis: AI models track industry-specific demand fluctuations, ensuring valuations reflect current market conditions.
- Linguistic characteristics: advanced models assess memorability, pronunciation ease, spelling simplicity, and brandability through NLP algorithms.
- Domain age: older domains often (yet not always) carry more value due to their established history and potential accumulated authority.
Technical Challenges and Limitations
Significant advances often mean significant challenges, both from the technical and strategic points of view.
Data limitations and biases
AI based appraisal systems are not exempt from the struggle of identifying domain sales data, including:
- Private transactions: many high-value domain sales occur privately with undisclosed prices, removing crucial training signals from the data ecosystem.
- Market volatility: domain valuations can fluctuate rapidly with technological and cultural trends, making historical data quickly outdated.
- Data skew: the data available tends to overrepresent certain market segments while underrepresenting others, potentially creating algorithmic biases.
Complexity of value determinants
Domains derive value from numerous interrelated factors that can be difficult to quantify:
- Subjective brandability: the perceived memorability or marketability of a domain contains subjective elements that remain challenging for algorithms to fully capture.
- Future potential: valuing domains often requires projecting future trends and use cases, which introduces inherent uncertainty regardless of algorithmic sophistication.
- Contextual value: a domain’s worth varies significantly based on the specific buyer’s context and intended use, creating multiple valid “correct” valuations for the same asset.
Algorithm Transparency Issues
Many commercial domain valuation tools operate as “black boxes,” providing estimates without explaining the reasoning or confidence levels behind them.
This lack of transparency makes it difficult for users to assess when an algorithm might be operating outside its zone of competence.
Security
With the rise of AI, security becomes more challenging.
Observing the information included in CSC’s 2024-2025 domain security report, we notice that:
Domain security remains a significant challenge, with 72% of the examined companies having less than half of the security measures implemented.
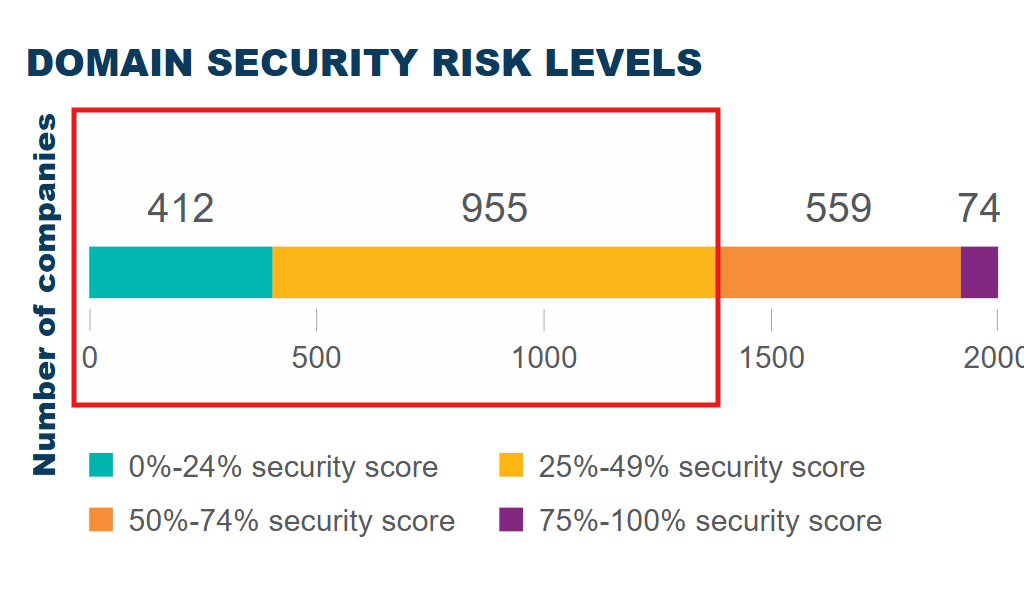
And,
- 112 of the surveyed companies have a domain security score of zero, indicating no adoption of any security measure.
- 45% of companies that use enterprise-class registrars also use registry lock
- Phishing attacks growing by more than 150% per year has helped increase the adoption of DMARC for email validation
Furthermore, ICANN and IANA are tackling the rise of AI-based cyber attacks (as well as the generally increased capacity of malevolent attacks to domains with AI).
Some of ICANN’s perspectives on domain security have been well expressed in the 81st edition of their Annual General Meeting (AGM).
For instance:
- Root Zone KSK System: ICANN has implemented stringent security measures for the Root Zone Key Signing Key (KSK) System, including restricted physical access to security tiers, implementation of administrative and personnel security measures, as well as firewalls and data protection systems.
- DNSSEC Implementation: ICANN advocates for the implementation of Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) as an essential step in addressing DNS security, including signing the DNS root zone.
- Geographical Redundancy: focussing on providing redundant sites in at least two geographically dispersed locations within the United States to ensure continuity of the IANA Naming Function in case of cyber or physical attacks, emergencies, or natural disasters.
- Security and Stability Advisory Committee (SSAC), which provides guidance on matters relating to the security and integrity of the Internet’s naming and address allocation systems, including operational, administrative, and registration issues.
Future directions of AI for domain valuation
The evolution of AI in domain valuation continues along several promising trajectories.
Enhanced Contextual Understanding
Next-generation valuation systems will likely incorporate greater contextual awareness, assessing domains not just on their intrinsic properties but on their alignment with specific use cases, industries, and brand identities.
This will require more sophisticated semantic understanding and market segmentation capabilities.
Real-time valuation adjustments
As AI systems gain access to streaming market data, valuations will become increasingly dynamic, adjusting in real-time to market fluctuations, trending topics, and emerging technologies.
This will transform domain valuation from a static estimate to a continuously updated metric.
Generative AI for domain suggestion
Beyond valuation, AI is also beginning to play a role in domain name generation and suggestion.
Advanced language models can propose domain names based on business descriptions or keywords, then immediately assess their potential market value in an integrated process.
Cross-Market intelligence integration
Future valuation systems will likely integrate insights from adjacent markets including SEO trends, brand value assessments, and even trademark analytics to provide more holistic domain value assessments.
From traditional appraisal and purchase to the all-in-one subscription approach
The domain industry needs to go beyond AI-driven valuation and revolutionize the entire domain lifecycle, from evaluation to purchase and seamless management.
For this, innovative solutions have been developed to switch from the traditional appraisal-purchase cycle to a more holistic approach.
For instance, through a membership-based model, it is possible to:
- Purchase domains at wholesale cost price, even in bulk
- Access domains appraised and offered in marketplaces like Sedo and Afternic
- Acquire and leverage security certificates
- Get discounts on domain and hosting licenses
- Manage and perform all domain-related operation from a single point of control
With AI-driven insights and an automation-first approach, the future of domain management is smarter, faster, and more profitable.


